By Julian Lee
It was too good to be true. Last weekend’s OPEC+ meeting took a decision in record time to extend deep output cuts that had halted a dramatic slide in prices — and members even agreed to abide by them. The timing was perfect. The deal would keep oil from flooding the market, allowing time for demand to recover as economies around the world fire back up after draconian coronavirus lockdowns.
Yet oil prices aren’t recovering as the bulls had hoped. Yes, there is a rebalancing of supply and demand in the offing, but consumption hasn’t picked up quite as much as they hoped it would by now.
A rally that briefly took West Texas Intermediate crude above $ 40 a barrel in the first week of June has fizzled out, as the euphoria of exiting lockdown is replaced by the reality of living with this virus. Around the world, it’s become clear that getting back to work and play will be halting. In the US, there are now fears a resurgence of Covid-19 infections in some places could force a reversal of reopenings. And new weekly data show record levels of inventories in US stockpiles.
It wasn’t supposed to be this way. Output cuts were meant to start draining inventories, while the reopening of stores, factories and businesses boosted demand. Instead, things seem to be going in the opposite direction.
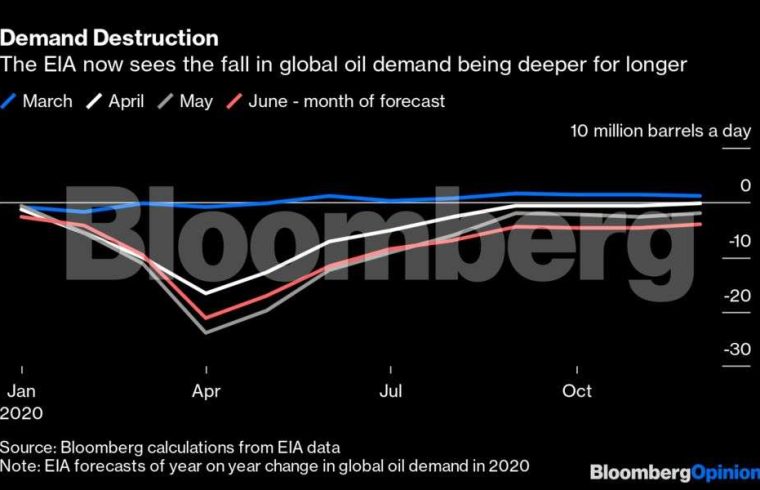
Let’s start with a broad view. The US Energy Information Administration’s outlook for global oil demand is becoming more pessimistic. Its latest forecast, published earlier this month, shows demand remaining almost 4.5 million barrels a day, or 4.5 per cent, below last year’s level in the fourth quarter. That’s twice the loss it foresaw last month.
Bloomberg
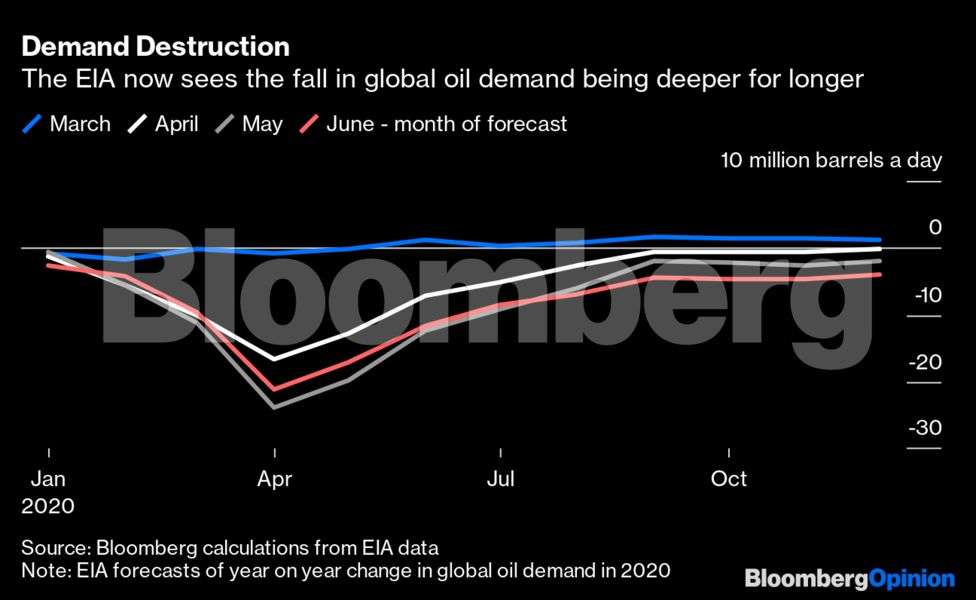
More specifically, in the US the recovery in oil demand from the depths of the destruction seen in April is faltering. Deliveries of all fuels from storage depots remain 20 per cent below year-earlier levels on a four-week average basis. The pickup in gasoline demand, as some people returned to work but shunned public transport, has ground to a halt and remains down year-on-year by about 20 per cent. Jet fuel is still down by more than 60 per cent, while the drop in distillate fuel oil demand is getting bigger, not smaller.
Bloomberg
Possible renewed lockdowns, if there were to be a second wave of infections, could quickly send the recovery into reverse.
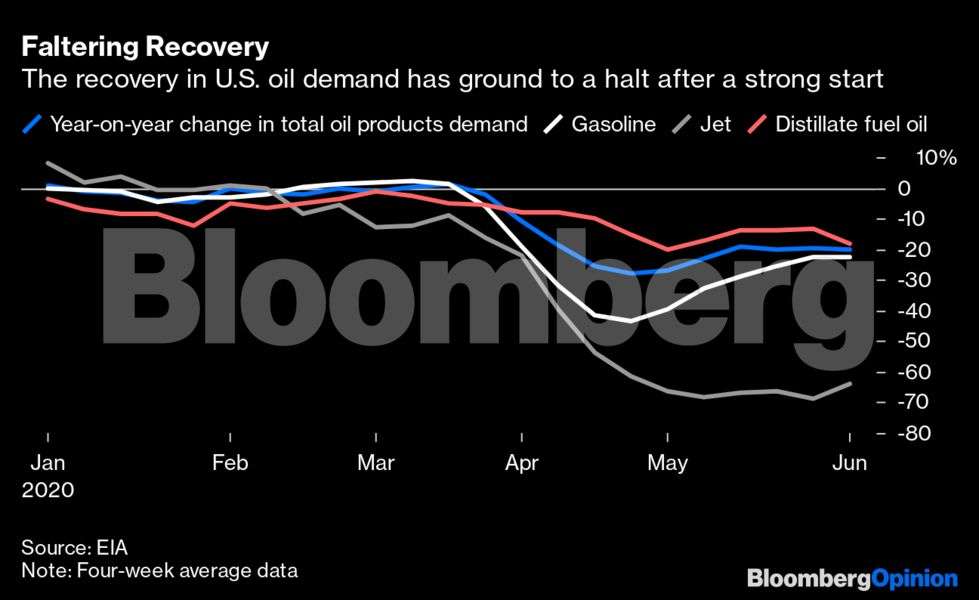
Now let’s take a look at transport, which combined accounts for 56 per cent of oil usage worldwide. There is definitely no sign of a V-shaped recovery in flying, which saw the biggest collapse as borders were closed and planes were grounded. Although worldwide commercial flights monitored by FlightRadar24 have risen by 54 per cent from their low-point in mid-April, they remain more than 60 per cent below the levels seen in early January.
While some airlines in Europe are beginning to reactivate routes, full border openings are still at least a couple of weeks away. In the U.K., quarantine requirements for arriving passengers are likely to limit the take-up of available seats.
Bloomberg
Private car usage is getting a boost as people seek to maintain their distance from each other. But it’s happening in a broader environment of greatly reduced mobility. Even as restrictions are eased, many companies are only welcoming a small percentage of their employees back into the office to respect social distancing measures. Many people who can work from home are continuing to do so.
This translates into a very narrow upturn in driving as shown in near real-time statistics from the Tomtom Traffic Index. Even in China, where some traffic has not only returned to, but exceeded, pre-pandemic levels, that congestion is limited in both time and space.
Bloomberg
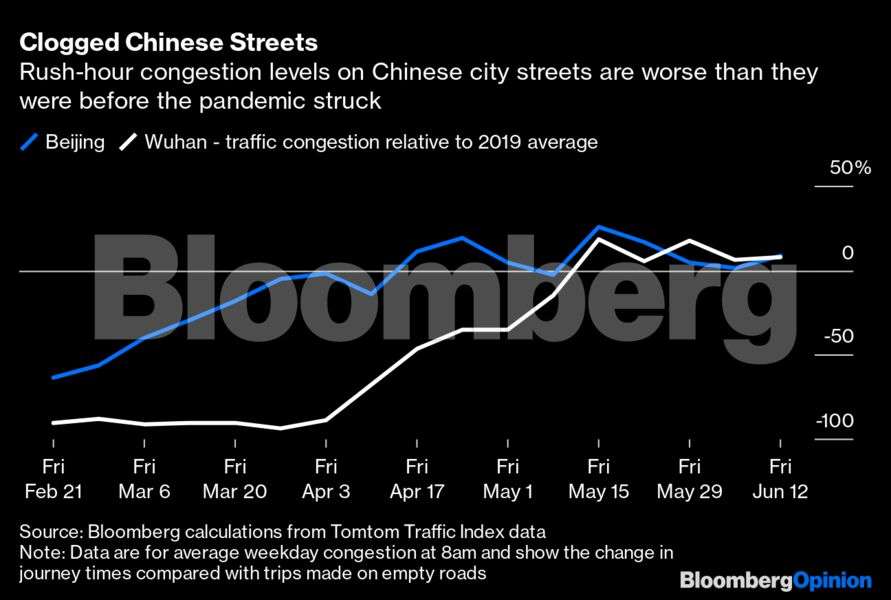
Roads in Chinese cities have become even more congested during peak commuting hours, as the chart above shows, but traffic volumes outside of those times, and during weekends and holidays, remains subdued, showing that things still aren’t fully back to normal.
Bloomberg
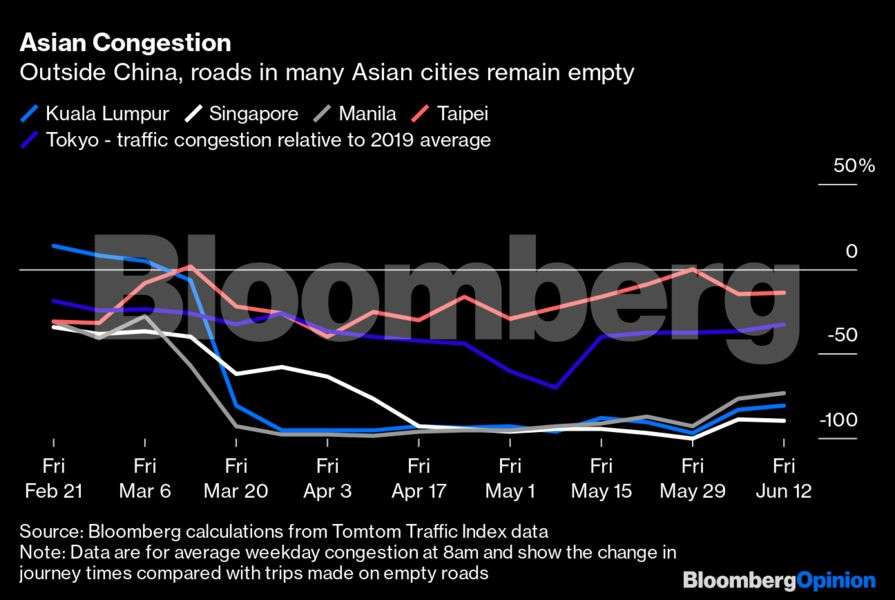
Elsewhere in Asia the picture is mixed. Traffic data for Japan and Taiwan show congestion never eased to the extent it did elsewhere. Roads in Taipei are almost as busy now as they were last year, while congestion in Tokyo is down by about 40 per cent. But roads remain quiet in Kuala Lumpur, Singapore and Manila, where vehicles are only just beginning to return to the streets.
Europe’s emergence from lockdown is reflected in the slow uptick in congestion levels on its city streets. Peak morning commute travel times are still around 65 per cent lower on average than a year ago in London and Milan, but in early April they had been down by almost 90 per cent. A recovery is beginning, but with many people choosing, or being asked by their employers, to continue working from home, the upturn is likely to be slow. A lack of parking facilities in European cities will probably also hamper a surge in car use like the one seen in China.
The US is further behind still. In New York and San Francisco, road congestion at 8 a.m. is still down by about 80 per cent from year-ago levels for a sixth week.
Bloomberg
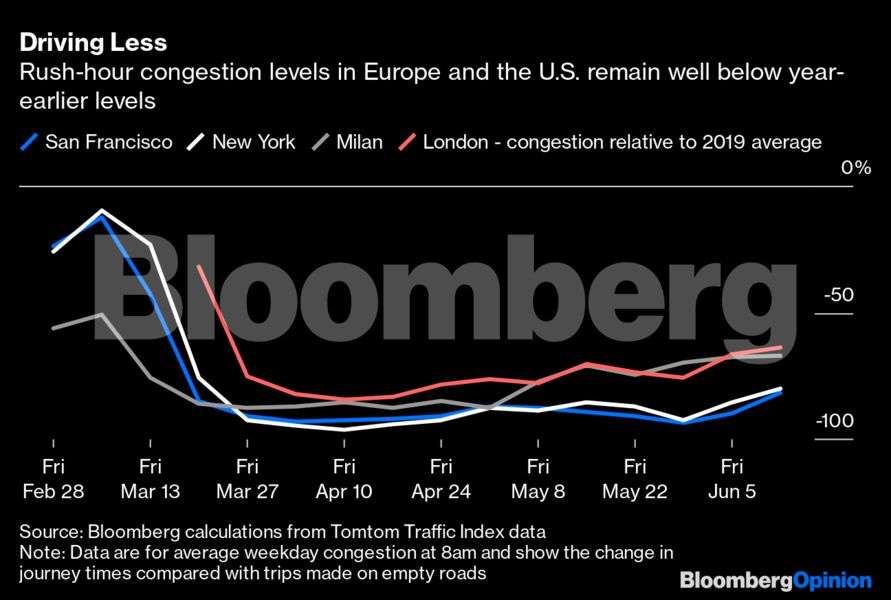
For those hoping that a quick, V-shaped recovery in oil demand would help spur oil prices higher, the data don’t appear very encouraging so far. There is still a long way to go before we get back to anything like normal.